Difference between revisions of "Selecting"
(→Geometric expressions) |
(→Geometric expressions) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
= Geometric expressions = | = Geometric expressions = | ||
| − | Of course one can select based on distances | + | Of course one can select based on distances: |
* '''display within(3.0,hydrophobic)''' Selects all atoms of hydrophobic residues, and all atoms within 3.0 Angstroms from these residues. | * '''display within(3.0,hydrophobic)''' Selects all atoms of hydrophobic residues, and all atoms within 3.0 Angstroms from these residues. | ||
| − | It is for the newest versions of Jmol also possible to select atoms according to [http://chemapps.stolaf.edu/jmol/docs/?#planeexpressions plane selections]. | + | It is for the newest versions of Jmol also possible to select atoms according to [http://chemapps.stolaf.edu/jmol/docs/?#planeexpressions plane selections]. |
| − | One can select atoms within 0.01 angstrom distance within a plane (and by combing two of these selections, on a line). | + | One can select atoms within 0.01 angstrom distance within a plane (and by combing two of these selections, on a line). To display atoms up to 6 Angstrom away from a surface with miller index 1 1 1, use: |
| − | * ''' ''' | + | * '''display within (-6, hkl, {1 1 1})''' |
| + | |||
| + | Using a plane definition instead, for example by defining two atoms and one xyz coordinate (in angstroms). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''display within (3, PLANE, (atomno=5) (atomno=40) {0 0 0})''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Or it is possible to draw a plane, define it, make it invisible, and then re-use the plane definition later on: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''draw plane1 (atomno=10) (atomno=40) {0 0 0};''' | ||
| + | * '''draw plane1 off;''' | ||
| + | * '''display within (-6, PLANE, $plane1)''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | One can first define two planes, then define the atoms enclosed by the two planes: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * '''draw plane1 (atomno=5) (atomno=40) {0 0 0}; ''' | ||
| + | * '''draw plane1 off;''' | ||
| + | * '''draw plane2 (atomno=5) (atomno=40) {20 20 20};''' | ||
| + | * '''draw plane2 off;''' | ||
| + | * '''display (within (-3, PLANE, $plane1) and within (3, PLANE, $plane2))''' | ||
= Topology expressions = | = Topology expressions = | ||
Revision as of 17:44, 12 September 2007
- A list of Jmol / JSmol Tutorials written by users.
- Using the mouse (English · Español · Français · Japanese).
- Scripting quickstart: rendering options · selecting atoms.
- How to create surfaces and isosurfaces, including cavities, pockets and tunnels.
- Displaying shapes, polyhedra, orbitals, dipoles, distances, forces and vibrations.
- Creating movies.
- Customizing Jmol: macros · menus.
- Web pages without writing code by using the Jmol "Export to Web" function.
Selecting can be done via atom expressions or based on topology or geometry.
The selection expressions used in Jmol can be used for the "select" and the "display within" commands.
Contents
Atom expressions
In the reference the full list of atom expressions can be found. Common examples:
- display *.CA displays all C-alpha atoms.
- select _C selects all carbon atoms, equivalent to select *.C??
- select [ALA] selects all atoms in ALA amino acids.
- display 1, this will select the first amino acid residue and/or molecule. If a file contains various molecules, and they are all numbered starting from 1, this will select all first molecules or first residues of peptide strings.
- display 1:A, if multiple chains are present, this will select residue 1 of chain A.
Geometric expressions
Of course one can select based on distances:
- display within(3.0,hydrophobic) Selects all atoms of hydrophobic residues, and all atoms within 3.0 Angstroms from these residues.
It is for the newest versions of Jmol also possible to select atoms according to plane selections.
One can select atoms within 0.01 angstrom distance within a plane (and by combing two of these selections, on a line). To display atoms up to 6 Angstrom away from a surface with miller index 1 1 1, use:
- display within (-6, hkl, {1 1 1})
Using a plane definition instead, for example by defining two atoms and one xyz coordinate (in angstroms).
- display within (3, PLANE, (atomno=5) (atomno=40) {0 0 0})
Or it is possible to draw a plane, define it, make it invisible, and then re-use the plane definition later on:
- draw plane1 (atomno=10) (atomno=40) {0 0 0};
- draw plane1 off;
- display within (-6, PLANE, $plane1)
One can first define two planes, then define the atoms enclosed by the two planes:
- draw plane1 (atomno=5) (atomno=40) {0 0 0};
- draw plane1 off;
- draw plane2 (atomno=5) (atomno=40) {20 20 20};
- draw plane2 off;
- display (within (-3, PLANE, $plane1) and within (3, PLANE, $plane2))
Topology expressions
Some examples of using topologies as selection criteria: (check the reference for more options)
- select molecule = 1 selects the first set of covalently bound atoms in the file.
- select connected(3) selects all atoms that are connected by bonds to 3 other atoms.
- select substructure("C(O)C") selects all ketone groups in the system. Any substructure strings in the SMILE format are accepted.
Combining selection statements
The combination of selection statements in Jmol is based on Boolean logic, using the statements And, Or, and Not, in a slightly different way than these are used in conversational language.
Example: We have a system consisting of water and a peptide chain. We are interested in selecting oxygen atoms. Let's call the set of atoms in the peptide chain A, and all oxygen atoms B.
Select A
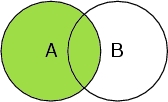 Selects all atoms in the peptide chain
Selects all atoms in the peptide chain
Select A or B
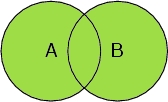 Selects all atoms in the peptide chain, and all oxygen atoms, including the oxygen atoms in the water molecules.
Selects all atoms in the peptide chain, and all oxygen atoms, including the oxygen atoms in the water molecules.
Select A and B
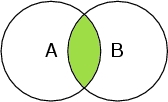 Selects only the atoms that are both belonging to the peptide chain, and oxygen atoms. Therefore it selects only the oxygen atoms in the chain.
Selects only the atoms that are both belonging to the peptide chain, and oxygen atoms. Therefore it selects only the oxygen atoms in the chain.
Select A and not B
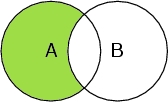 Selects the atoms in the peptide chain, but not the ones that are oxygen atoms.
Selects the atoms in the peptide chain, but not the ones that are oxygen atoms.
Select (A or B ) and (not (A and B))
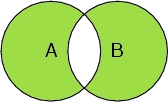 Selects all the peptide chain atoms and all the oxygen atoms, but not the oxygen atoms in the peptide chain.
Selects all the peptide chain atoms and all the oxygen atoms, but not the oxygen atoms in the peptide chain.