Internationalisation/Offline/Export to Web
Contents
Translating the Export to web module
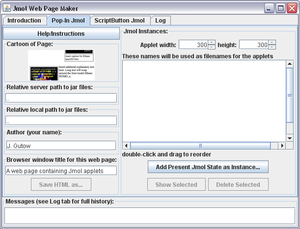
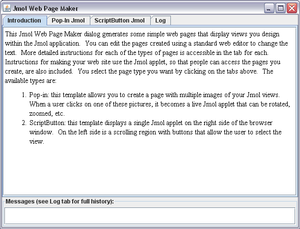
The Export to web module ![]() ,
part of the Jmol application, consists of an interface
(a window entitled Jmol Web Page Maker that opens separate from the
main app window and can be operated in parallel),
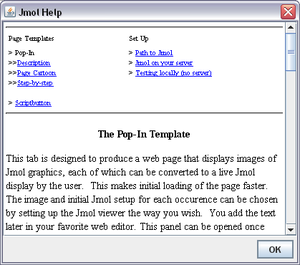
a help window,
and a set of internal templates that will be used to generate the
user's web pages.
All of them need translation, with a different procedure.
,
part of the Jmol application, consists of an interface
(a window entitled Jmol Web Page Maker that opens separate from the
main app window and can be operated in parallel),
a help window,
and a set of internal templates that will be used to generate the
user's web pages.
All of them need translation, with a different procedure.
Translating the interface
The Jmol Web Page Maker window contains several texts that are translated in the
same way as the rest of the application (either online through Launchpad web site,
or offline by editing the ![]() LANG.po files on your computer; see
Translating the application/applet).
LANG.po files on your computer; see
Translating the application/applet).
Translating the instructions
The introduction panel (a tab inside the Jmol Web Page Maker interface) and the help/instructions panels (opened in a separate window) are built from html files.
- These files are in
org/openscience/jmol/app/webexport/html/ - Currently:
 Installing_Applet.html
Installing_Applet.html Path_to_Applet.html
Path_to_Applet.html pop_in_instructions.html
pop_in_instructions.html script_button_instructions.html
script_button_instructions.html Testing_Pages_Locally.html
Testing_Pages_Locally.html WebExportIntro.html
WebExportIntro.html
You must duplicate those original English files and rename them according to your language, then translate their content using a text or html editor. See Translating html files.
Translating the web page templates
Translating the html files
The templates are composed of several html files.
- These files are in
org/openscience/jmol/app/webexport/html/ - Currently:
 pop_in_template.html
pop_in_template.html pop_in_template2.html
pop_in_template2.html script_button_template.html
script_button_template.html script_button_template2.html
script_button_template2.html
You must duplicate those original English files and rename them according to your language, then translate their content using a text or html editor. See Translating html files.
Translating some terms showing in the final web pages
Some text strings are shown in the final web pages but are not included in the html template files themselves. Instead, they are included in the PO files (the same as text for the interface is). However, given that they will be shown in html files and not within the application, special precautions are needed to assure the proper visualization in any user's browser.
You must provide translated text strings (using either the online or offline methods) that do not use accented characters per se, but converted into the equivalent HTML entities. Examples:
á or á for accute-accented a (á) é or é for accute-accented e (é) í or í for accute-accented i (Ã) ó or ó for accute-accented o (ó) ú or ú for accute-accented u (ú) ñ or ñ for tilde-n (ñ) ¿ or ¿ for opening question mark (¿) ¡ or ¡ for opening exclamation mark (¡)
(see http://htmlhelp.com/reference/html40/entities/ for a full list of entity codes)